BPA In Cans – Do All Tins Contain Bisphenol A?
Packaging in the modern world plays a pivotal role in shaping consumer experiences, ensuring product integrity, and contributing to sustainable practices. As consumers, we encounter packaging in various forms such as tin cans and bottles. However, packaging is not only limited to its practical purpose of protecting and containing goods, but it also serves as a crucial marketing tool and communication medium. For example, in today’s world, plastic packaging is considered environmentally harmful and not sustainable. So, in order for companies to look eco-friendly, they have switched to more sustainable options such as tin containers and biodegradable packaging solutions. In this contemporary era, packaging has evolved to reflect consumers' changing needs and preferences, embodying innovation, sustainability, and convenience.

Undoubtedly, the innovation and availability of modern packaging solutions such as tin containers and plastic bottles have been essential in propelling us to the industrial heights we currently occupy. It paved the way for an unparalleled magnitude of production, distribution, and utilization of goods unimaginable before. However, this unprecedented progress in packaging technology comes with its share of challenges and concerns. The adverse effects on human health are a major concern, given the increasing use of single-use plastics and tin cans that contain BPA, which raises significant health concerns.
What Does BPA Stand For?
Before delving into the effects of BPA, it is important to know what does BPA stand for and its properties. Bisphenol A, commonly known as BPA, is a chemical compound widely used in manufacturing certain plastics, including food and beverage tin containers, water bottles, and even baby bottles. BPA is mainly utilized to make plastics strong and resilient. Its chemical structure comprises two phenol functional groups and is extensively employed in the manufacturing of polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins. BPA in cans or epoxy resins is used to keep the inside of the can from corroding and reacting with food. BPA's chemical properties make it accessible for a wide range of applications in consumer products, as its ability to enhance the material's durability, clarity, and protective qualities is hugely appreciated in the packaging industry. However, as with any other thing, BPA also has some problems. Several scientific studies have raised concerns over the adverse effects of BPA in the event of consumption.
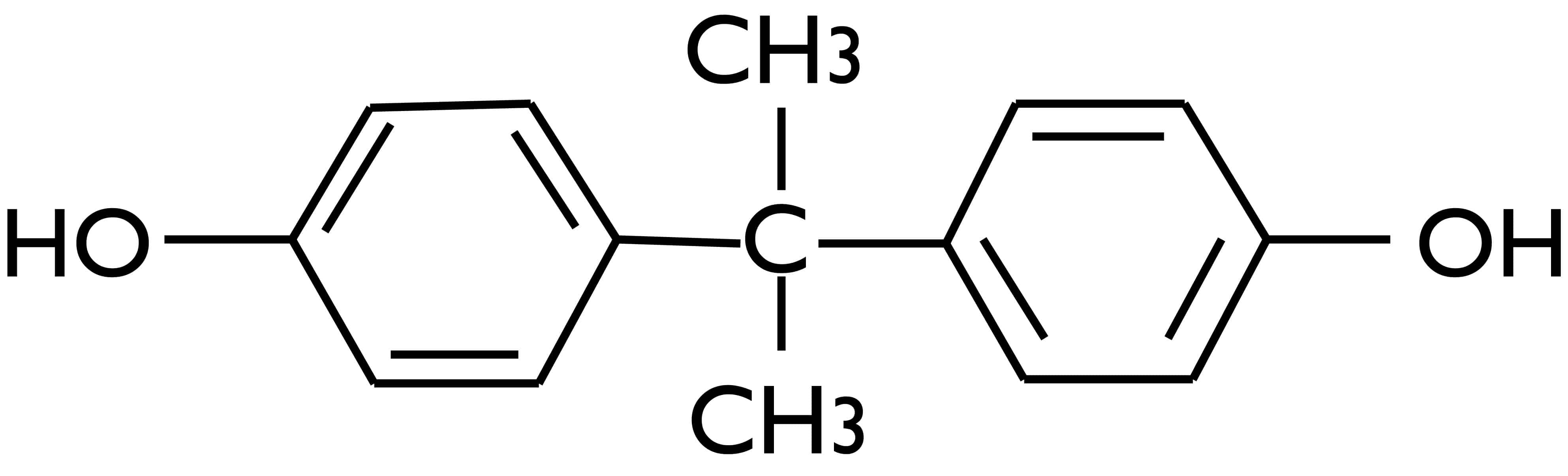
Evidence suggests that food and drinks may become contaminated with BPA in cans, particularly when tin containers are heated or encounter acidic situations. The presence of BPA in the food chain poses a significant threat to consumer health, causing discomfort among them. One major concern is its ability to mimic or interfere with natural hormones in the body, such as estrogen. BPA is an endocrine disruptor, which means it can disrupt the normal functioning of the hormone system and lead to various health issues. There is a higher chance of experiencing reproductive abnormalities, developmental complications, and specific diseases due to this process, known as hormonal mimicry [1]. Furthermore, according to research, BPA can also cause mental issues in humans, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and cardiovascular problems like high blood pressure and heart disease [2].
A multitude of nations have prohibited the inclusion of BPA in cans, bottles, and food tin containers. Additionally, there is an increasing demand for BPA-free products and alternative packaging materials that do not pose similar risks to human health.
Presence Of BPA In Cans
BPA is frequently present in the coatings of metal tin cans, especially those utilized for packaging food and drinks. The primary reason for using BPA in cans is to create a protective barrier between the contents and the metal. This barrier helps prevent tin containers from corrosion and maintains the quality and safety of the packaged products. The presence of BPA guarantees that the taste and quality of the food or beverage are safeguarded as it forms a resilient and effective lining, protecting them from the metal throughout their shelf life.

The presence of BPA in cans has sparked concern, as it can leach into packaged food or drink, especially under specific conditions like high temperatures or acidity. Depending on the manufacturing processes and materials used, the levels of BPA in various types of tin containers, like those for canned drinks or canned food products, may differ. This leaching raises health-related questions as BPA is known to exhibit endocrine-disrupting properties. Thus, the rising concern for health and changing consumer preferences towards greener packaging options have led to an increasing demand for metal packaging alternatives that are free from BPA. Manufacturers are exploring and adopting alternative tin cans and coatings that maintain the protective benefits of BPA without the associated health risks, contributing to a shift in the landscape of metal packaging in the modern era.
Different Type Of Tin Cans
Metal packaging is a diverse and versatile category encompassing various types of tin containers made from metals such as steel, aluminum, and tinplate. These materials enable an array of packaging solutions that cater to different needs and industries, ranging from food tin cans and beverages to medical and personal care. In the food industry, BPA-free tin cans offer excellent durability and a long shelf-life for products such as canned vegetables and soups, while aluminum cans provide lightness and convenient portability for beverages like soda and beer. Tinplate is commonly used in the form of tin cans for metal packaging for items like aerosol sprays and paints due to its corrosion resistance and formability. The use of various metals in packaging ensures a wide range of options that meet various functional requirements, making metal packaging a pivotal component in today's complex consumer product landscape. Some of the metal tin containers solutions are discussed in detail below:
1) Food Containers: Metal food tin containers play a crucial role in preserving and packaging various food products, providing a durable and protective solution for both storage and transportation. Tin cans, a classic form of metal packaging, have been a staple in the food industry for decades. Traditionally composed of steel coated with a thin layer of tin, these cans create a reliable barrier against external elements, preventing corrosion and maintaining the freshness of the enclosed food. However, using Bisphenol A (BPA) in cans for the linings of some tin cans has raised health concerns, as BPA can leach into the food. Consequently, there is a contemporary push within the industry to develop BPA-free alternatives, ensuring that potential health risks do not compromise the benefits of tin cans in food packaging.
2) Tin Cans: Tin cans are a timeless and versatile form of metal packaging in markets. Historically, these cans were made primarily of tin-plated steel, offering durable and corrosion-resistant tin containers for a wide range of goods. However, as the industry has evolved, modern tin cans often feature other materials, such as aluminum or are coated with BPA-containing linings for enhanced preservation.
3) Drinks: Metal packaging, particularly aluminum cans and tin cans, has become synonymous with the beverage industry, providing a lightweight and efficient solution for packaging drinks. Aluminum cans offer excellent protection against light and air, preserving the flavor and quality of the beverages inside. While the aluminum itself does not contain BPA, concerns arise from the potential presence of BPA in cans that are used to protect against acidity and maintain product freshness. In response to consumer preferences for healthier and more sustainable options, the beverage industry is actively exploring and implementing BPA-free tin containers.
Aluminum Tin Cans

Aluminum tin cans, a modern evolution of traditional tin-plated steel cans, have become a hallmark in the packaging industry due to their exceptional properties and numerous advantages. Because aluminum has a distinct property, it eliminates the necessity of a Bisphenol A (BPA) in cans, unlike steel tin containers. With a natural oxide layer forming, aluminum inherently exhibits non-reactive tendencies, effectively creating a protective shield between the can's metallic surface and its contents. This property eliminates the necessity for BPA-containing linings, addressing health concerns associated with BPA leaching into packaged goods. The non-reactive nature of aluminum ensures that the integrity and purity of the enclosed products remain intact without compromising consumer safety.
The advantages of using aluminum tin cans extend beyond their BPA-free nature. These cans provide an unmatched shield from rust and oxidation, assuring the extended life and crispness of the enclosed products. The corrosion-resistant properties of aluminum make it an ideal choice for preserving the contents of the can, whether it be food, beverages, or other goods. The lightweight yet durable nature of aluminum tin containers also contributes to cost-effective transportation and storage, making them an environmentally friendly option. As consumer awareness of health and sustainability grows, the use of aluminum tin cans exemplifies a commitment to both product safety and eco-conscious packaging practices in the dynamic landscape of modern packaging.
How To Tell If Cans Are BPA-Free

We all know how harmful BPA is, but now it's time to shed some light on what is BPA-free and how to identify BPA-free cans. It involves a comprehensive approach encompassing label scrutiny, material awareness, and staying abreast of brand practices. Firstly, consumers should thoroughly examine tin cans packaging labels for explicit indications of "BPA-free," a feature increasingly emphasized by responsible manufacturers to meet the rising demand for BPA-free options. Additionally, checking recycling codes on the tin containers bottom, understanding the inherent properties of materials such as aluminum cans and tin cans, and contacting manufacturers directly for information on their packaging materials contribute to making informed choices about BPA content.
Staying informed about industry trends is pivotal in the quest for BPA-free packaging. As awareness of potential health risks associated with BPA in cans grows, more companies will shift towards BPA-free alternatives. Regularly updating oneself on industry practices and utilizing apps or online resources that provide information on BPA content empower consumers to navigate the evolving landscape of packaging materials and make choices aligned with their preference for BPA-free tin cans.
